How To Install Amanda Backup On Centos
Contents.Advanced Maryland Automatic Network Disk ArchiverTraditionally, backups have been scheduled as a Full dump of everything on the weekend, then incremental backups throughout the week. There are several disadvantages to this strategy:.
The backup time on the weekend is much longer than during the week. The tape usage during the week is very small, but because the backups on the weekend are very large you must have very large tapes. This means wasted tape during the week. To recover an entire directory from Friday requires Sunday's, Monday's, Tuesday's, Wednesday's and Thursday's tapes.Amanda changes that paradigm. The primary goal for Amanda is to balance tape usage each night. To do this, it varies the days on which certain backup 'entries' (more on this later) are dumped in full, so that each night the amount of data that is backed up is more or less equal. This means:.

The backup time is approximately the same every night. The tape usage is uniform, so a smaller drive can be used and no tape has to be wasted.To recover an entire directory from Friday may only require one tape at best, and a dumpcycle's worth of tapes at worst (more on this later as well).Throughout this document, you will see references to 'tape' quite frequently.
Install Amanda Debian 9
Know that this does not necessarily mean magnetic tape. Amanda supports backing up to hard disk (via the file driver) or even a RAIT feature, which could be multiple tapes, multiple hard disks, or a combination thereof.Important TermsWhen talking about any subject, it's good to have a common vocabulary. Below are some important terms that should be understood. Level 0A full dump, or back up, of a set of files. This means that every file is saved for later retreival.
Level 1The first incremental back up of a set of files. This means that only the files that have changed since the last Level 0 have been stored for later retreival. Level nThe incremental backup of files since the last Level n-1 backup. Note: Levels can sometimes be difficult to understand, so there is an available. Disklist Entry (DLE)Amanda stores the items to be backed up in the disklist file, so each item becomes a Disklist Entry. Dumpcycle The maximum length of time that a DLE receives a Level 0 backup.
(Usually 1 week) runspercycle The number of times during a dumpcycle that Amanda will be run. (Usually 7 for every night of the week or 5 for every weeknight, assuming a dumpcycle of 1 week) tapecycle The number of tapes Amanda must use before 'recycling' tapes.
(Ideally this should be at minimum 2.runspercycle+1. That way you have two complete sets of backups, plus an extra tape if something goes wrong)Amanda is a schedulerOften the question is asked: 'Will Amanda support my ACME Tape Drive 2000 Ultra Professional?' The answer is: 'Does your Operating System Support it?'
The reason for this is that Amanda doesn't actually talk directly to the tape drive. It depends on Operating System utilities such as dd, tar and the many flavors of dump to do that. Amanda merely calculates the appropriate data to be backed up based on the parameters set and schedules it appropriately. How are things scheduled? The definitions above should provide a hint, but we'll explain it a little more in this section.Amanda schedules backups mostly based around the three variables listed above; dumpcycle, runspercycle, and tapecycle.
Amanda ensures (to the best of its ability) that each individual DLE receives at least one Level 0 backup per dumpcycle. It is at least one, because Amanda may 'promote' a dump to receive a Level 0 ahead of its regularly scheduled time (remember the primary goal of Amanda - to balance tape usage) to help balance the size of the data. The runspercycle variable lets Amanda know how many chances it has to fit everything in during a dumpcycle. Tapecycle is a safeguard to make sure you don't overwrite data that you shouldn't overwrite yet.Amanda on CentOSA long time ago, a decision was made to not require any configuration to be done on Amanda clients. This is good if you back up several hundred machines, however it has the drawback that certain options must be compiled into the client binaries. Among these are the address/hostname of your tape and index servers.
This presents an interesting problem for those who package binaries for Amanda (e.g. Just about every Linux distribution); they can't know settings at compile time, so some assumptions must be made. The biggest problem with that is using localhost as the server names.

(See the for details on why this is a problem). Because of this it is recommended to rebuild the Amanda RPMs for your specific environment.Recent releases of Amanda (2.5.1 and above) have broken with tradition and now can use a configuration file on the client. See for details on this file.For CentOS 3 and 4, changing the defaults requires editing of the.spec file. In CentOS 5 and forward, changes to the.spec file have been made upstream to ease this problem. Specifically, the variables%defconfig,%tapeserver and%indexserver are now configurable through a define (e.g. Rpmbuild -rebuild -define 'defconfig Dailies' -define 'tapeserver fqdn.com' amanda-2.5.0p2-4.i386.rpm)For those of you who don't wish to rebuild a 2.4.5 or later version of Amanda on your CentOS 3 or 4 system, here's how you can rebuild the existing packages for your environment (using CentOS 4 as an example):.
Download the amanda-2.4.4p3-1.src.rpm file.Install the source rpm: rpm -i amanda-2.4.4p3-1.src.rpm. This will extract the contents into your rpm directory (see for help on setting up your build system). Edit the SPECS/amanda.spec file to reflect the appropriate servers, and any other changes you might want to make. It is also suggested that you change the Release: tag to indicate you've made changes (using initials or something similar). Rebuild the rpms: rpmbuild -ba SPECS/amanda.spec.
Enjoy your freshly customized RPMsLinks.Latest ReleaseThe current stable release is available at.HowTos/AmandaBackups (last edited 2010-09-29 05:15:08 by ).
When it comes to data safety and security, not only large companies, but also personal computer owners also need to have good backup and recovery software that protects their data from losing their precious data. To overcome these issue, there are a lot of open source backup software tools that are available that can help protect your data. And nowadays, computer desktops come with huge storage capacity and in turn it means lots of data being stored. This also leads to a huge risk of losing all the data if the system gets crashed and it may take several days and weeks to recover and repair the damage cause. Hence it is increasingly important to have a proper recovery solution with you all the time.In this article we are going to review some of the top 12 open source back up tools for Linux systems. 1) BaculaWhen it comes to open sources backup tools for linux systems, Bacula is one of the most widely used and popular backup and recovery solution for linux system.
It also helps in verifying the data across different computer networked systems effectively. Bacula comes with an effective and advanced storage management solution that helps you to recover all lost and damaged files pretty much quickly when compared to other backup and recovery solutions. It is the complete backup solution that is needed for a small or even a large enterprise to maintain and secure their data. Bacula comes with two versions, the Basic and Enterprise version. The basic version comes with all the basic features needed in a backup and recovery solution and the enterprise version comes with a lot of advanced features including Metal backup, cloud back and also backup solutions for VMs.
2) DuplicatiDuplicati is another popular linux open source backup solution that is available completely free even for commercial usage. It is designed to run in various operating systems including Linux, Windows and MacOS. With Duplicati, you can easily take online backups and comes with a pause/resume feature to pause the backup process during any network issues and will automatically resume backup once the issue is rectified and the process continues from where it stopped.
Duplicati also conducts regular checks on the backups to detect for any broken/corrupt backup. All backups are provided with an AES-256 encryption and all backups are compressed and stored on the servers. 3) rsnapshotrsnapshot is a great filesystem snapshot tool that is capable of taking incremental backups in both local and remote filesystems. It is an rsync based backup system that can be used to take backup for any number of machines in the network. Since rsync is cleverly designed to use hard links, the disk space in your system is effectively used. By hardinks, it means even though it looks like taking a complete backup everytime, it only takes a full backup and then only the differences are backed up to save more space.
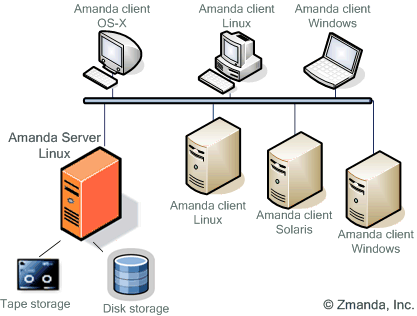
With ssh, rsync can be used to take snapshots of remote systems as well. 4) AmandaAdvanced Maryland Automatic Network Disk Archiver also called as Amanda is another great open source backup and recovery software for linux systems. It is basically an enterprise grade backup solution and according to the company, Amanda is running on around a million servers and desktops worldwide across various operating systems including Linux, Windows, UNIX, MacOS, BSD etc., Amanda comes in three different editions including Community edition, Enterprise edition and Zmanda Backup appliance.
The community edition is freely available for download whereas the enterprise edition supports live application backups and databases. The Zmanda backup appliance is a virtual machine that is capable of backing up an entire network easily. 5) rsync (Command line tool)Rsync is another popular linux open source tool that helps in quick incremental file transfers. Rsync can help you to transfer files to local host to remote host and vice-versa. The remote-update protocol enables the speedier file transfers as it checks if the destination file already exists and stops copying the file again. The delta-transfer algorithm also enables it to sync remote files easily and quickly as it doesn’t send the overall file, but only the differences are only sent and hence the sync is pretty much quick.
6) BackupPCBackupPC is another enterprise range open source backup tool that supports all major operating systems including Windows, Linux and Mac. It is also a high performance backup system that utilizes compression and pooling setup that greatly reduces the disk storage along with disk I/O. 7) Rear (Relax & Recover)Relax and Recover also called as Rear is largely kind of a setup and forget utility as you don’t need to do anything after installing the utility in your system as it takes care of backing up and restoring files when needed automatically.
Amanda Backup Software
The design is completely modular and easy to use and supports various boot media types including USB, eSATA, PXE, ISO and OBDR etc. It also supports both tar and rsync internal backup methods.Read More on: 8) ClonezillaClonezilla is a great backup and cloning utility that can help you clone or take an image of an entire partition or a disk easily. It is available in two versions including the Clonezilla Live edition and Clonezilla SE edition. It is a complete free and open source backup utility and the Live edition is ideal for taking backup and restoring of single systems whereas the SE or the server edition is perfect to take huge server backups.
How To Install Amanda Backup On Centos 10
One of the important features of this cloning utility is that it only used blocks and restored in the hard disk and thus enhancing the cloning efficiency. 9) Back in TimeBack in Time is an rsync based backup utility that comes with an interesting feature of using hard links during the backup process.
Since hard links are used in this backup utility, it is easy to remove old snapshots by looking at the snapshots at regular intervals. Back in Time also doesn’t allow compression. 10) Bareos – Open Source Data ProtectionBareos stands for “ Backup Archiving Recovery Open Sourced” is an open source backup software that can be used to take efficient backup and restoring of computer and can take backups in different media’s including tape backups and disk backups. It enables the system administrator to easily manage all kinds of backup, restore and data verification of computers of an entire network. 11) Box BackupBox Backup is the next open source backup utility in our list that only copies or backups the files into the disk only.
It doesn’t support other kind of backups including tape or disk backup. It comes with strong encryption features and also uses only minimum bandwidth. The backup utility is totally automatic and fully secure. 12) sbackup (Simple Backup Suite)sbackup or Simple Backup solution is that is primary developed as a desktop backup utility. Sbackup can be used to take frequent backups of your files and directories and it also utilizes regular expressions to exclude files that are already copied.
It supports compressed archives and hence it can be used for taking backup of huge data. Even though it is popular among users for its predefined backup solutions, it can also be used for manual, scheduled and custom backups. But sbackup only comes with a backup solution and doesn’t have any restore feature.